Interventional Radiology
A sub-specialty of radiology, Interventional radiology - IR has contributed significantly to medical developments in recent years. Patients are diagnosed and treated using minimally invasive imaging techniques such as X-ray, MRI and ultrasound for guidance. In addition to diagnosis, new treatment options are offered by techniques in Interventional radiology (also known as Surgical Radiology)- patients are treated with lesser risk and shorter hospital stays.
The advantage of IR procedures is that they can be used in almost every organ system - be it abdomen, central nervous system, chest, heart and vascular, musculoskeletal, genito-urinary and other organs and soft tissues.
Interventional Radiologists
Patient evaluation and management are provided by Interventional radiologists, who are doctors trained in radiology and in minimally invasive procedures, skilled in interpreting X rays, ultrasounds and CT and other imaging techniques. While surgery was the only available option for a number of conditions a few years back, these days the expertise of Interventional radiologists with imaging technique enables them to guide small catheters, that are only a few millimeters in diameter and guide wires through blood vessels or other organ pathways to treat many conditions. Diseases and conditions are diagnosed and treated percutaneously with minimally invasive procedures.
Benefits and uses of Interventional radiology
This is an imaging technique using cutting-edge equipment for accurate diagnosis and treatment, a minimally invasive procedure through a small nick in the skin, minimizing the patient's discomfort and recovery time. These days, there is hardly any area in hospital medicine where IR has not impacted patient management.
These procedures require only local anesthesia, and short stays at the hospital. Sick patients who are unfit to undergo surgery can also undergo these techniques. Recovery post IR procedure is less painful than when the patient undergoes surgical procedures.
These image guided medical procedures use CT, MRI, fluoroscopy and ultrasound to view targeted areas. This makes the vessels clearly visible under imaging. A thin catheter is used to deliver the contrast material into a particular blood vessel and shows the inside of the vessel allowing the radiologist to locate blockages. Some examples of interventional radiology procedures include:
- Angiography or Angioplasty
- Stent placement
- Control bleeding with Embolization
- Tumor embolization
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Needle biopsies for different organs including lungs and thyroid gland
- Tumor ablation
- Breast biopsy by stereotactic or ultrasound techniques
- Uterine artery embolization
- Feeding tube placement
- Venous access catheter placement
Using Interventional radiology
By minimizing the physical trauma to the patient, non-surgical interventions also reduce infection rates and recovery time and shorten hospital stays.
- Blood vessel disease such as narrowing of arteries leading to restricted flow of blood
- Expanded arteries at risk of rupture and bleeding
- Bleeding or hemorrhage which is the most common vascular emergency treated by IR.
- Blood clots in the lung
- Dilated veins or varicose veins that most commonly occur in the legs but can occur in the pelvis and scrotum and can be treated by blocking the vein by heat treatment or using embolization techniques.
- Tumor therapies in liver intended to shrink or destroy them in their primary site.
- Kidney and other tumors by destructive therapies
- Uterine fibroids which cause heavy menstrual bleeding and pain caused by benign tumors called fibroids
- Kidney stones that can cause pain
- Infection and blockage in the kidney and gall stones, one of the most common upper abdominal disorders.
CBCT Scan
CBCT, also known as C-arm CT, Cone Beam Volume CT or flat panel CY is a medical imaging technique, like a conventional CT scan. It provides fast and accurate visualization of bony anatomical structures in three dimensions. It is essentially X-ray computed Tomography where the X rays are divergent, forming a cone. Unlike traditional dental x-rays that are flat images, CBCT scan can provide multiple images of the teeth, soft tissues, bone and nerve pathways. The image quality is better due to reduced scatter radiation. These images help compile exact 3D images of various angles of the face and jaw. It also allows the dentist to zoom into specific maxillofacial structures with alternate angles for clearer evaluation.
CBCT applications
CBCT is important in planning and diagnosis in implant dentistry and interventional radiology among other things. In dentistry, it is used in oral surgery, endodontics and orthodontics.
CBCT is an important tool in image-guided radiation therapy for patient positioning and verification. Nearly 600 distinct images can be captured by rotating the CBCT scanner around the patient's head. In interventional radiology, a single 200 degree rotation over the region of interest provides volumetric data. The scanning software collects the data and reconstructs it, producing a digital volume composed of three dimensional voxels of anatomical data that can be manipulated and visualized with specialized software.
CBCT offers invaluable information in planning and assessment of surgical implants. A dental cone beam scan is the preferred method for pre surgical assessment of dental implant sites. Since CBCT is a 3D rendition, there are several structures that can be viewed with this facility, which are not available with conventional 2D radiology. CBCT offers an undistorted view of the dentition. That is why it is used for accurately visualizing both erupted and non erupted teeth. It is also used in tooth root orientation and anomalous structures.
Use of CBCT in Interventional Radiology (IR)
The scanner is mounted on a C arm in the IR suite offering real time imaging. Since this can be done on a stationary patient, it eliminates the time spent to transfer a patient from the Angiography suite to a conventional computed Tomography scanner. It also facilitates many applications of CBCT during IR procedures. Both primary and supplementary form of imaging can be done with CBCT. For fluoroscopy and soft tissues, it can be very helpful during complex procedures to reduce patient's radiation exposure.
Clinical applications of CBCT
In hepatocellular carcinoma, CBCT contrast confirms that the proper artery is selected to deliver the therapy. For benign prostatic hypertrophy BPH, CBCT provides soft tissue details needed to visualize prostatic enhancement, identify duplicated prostatic arteries and avoid non target embolization. During abscess drainage, CBCT confirms needle tip location after placement under ultrasound and confirms drain placement by revealing contrast injection into the desired location.
For adenoma adrenal vein sampling, contrast enhanced CBCT shows perfusion of the adrenal gland to confirm catheter placement for obtaining a satisfactory sample. During stent placement, CBCT improves the visualization of intracranial and extracranial stents. CBCT guides needle placement and allows diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity and specificity in lung nodules. After correction of vascular anomalies, CBCT sensitively detects small infarcts in tissue during the procedure to prevent further shunting.
Risks
Although it is a compact, faster and safer version of the regular CT, dental CBCT delivers more radiation than conventional dental X rays. Even properly shielded CBCT exposes patients to radiation many times more than 2D digital dental x rays. However, improved outcomes at lowered cost and time saving, reduced morbidity and reduced need for exploratory procedures and other such benefits of CBCT continue to make it popular with practitioners.
Cerebral hemorrhage
Cerebral hemorrhage also known as stroke is associated with ischemic conditions. These types of conditions often occur when the brain experiences shortage of blood supply. The brain cells get damaged as a result of bleeding internally. There are several types of cerebral hemorrhage caused in different regions of the brain. The most predominant type of cerebral hemorrhages include:
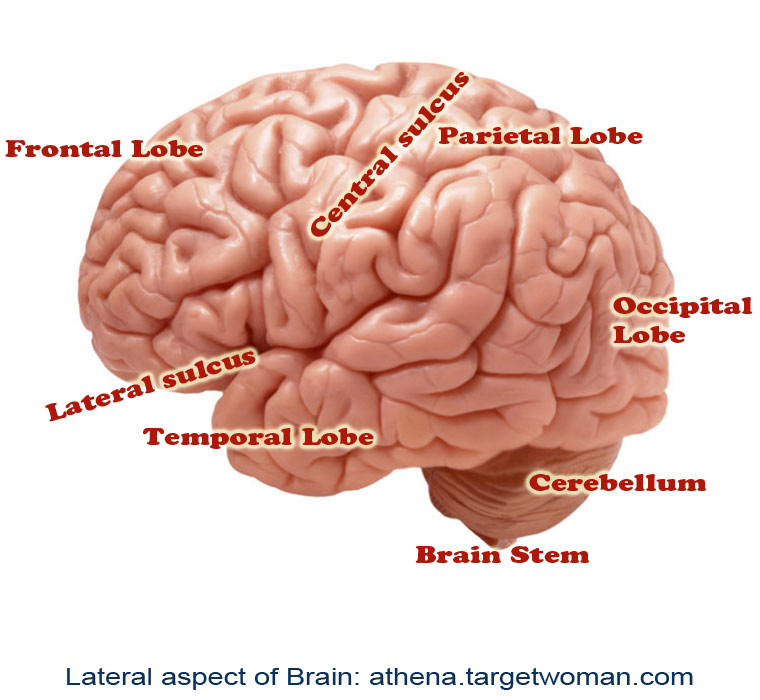
Intra cerebral hemorrhages: In this condition the brain experiences internal bleeding and it occurs in the region of the cerebellum depending upon the zone of injury that leads to the bleeding. The parenchymal tissues of the brain undergo severe damage in this condition.
Subarachnoid hemorrhages: This type of bleeding is caused between the membranes lining the brain.
Subdural hematoma: This is commonly found in athletes such as boxers and wrestlers. The injury or trauma is caused to the veins underneath the dura of the brain.
Epidural hematoma: This is also a condition caused because of trauma or head injury. The meningeal artery is ruptured leading to bleeding in the region between skull and membrane covering the brain.
Other forms of damage caused to the brain predominantly include ventricular damage which is caused because of trauma to the ventricles of the brain which contain the cerebrospinal fluid.
Causes of stroke
Cerebral hemorrhage or stroke may occur because of many reasons. In most forms it is closely associated with congenital abnormalities of the brain and also because of trauma or altered lifestyle patterns. Some of the common conditions that cause cerebral hemorrhages are aneurysms; deformities in the arterial and venous supply to the brain, presence of abnormal proteins such amyloids which lead to deterioration of brain cells and hypertension.
Symptoms
The major risk factors for cerebral hemorrhage are hypertension, trauma and alcoholism. This condition mostly occurs in patients who have a history of diabetes, habits such as alcoholism, smoking and aged people. Many patients experience numbness in their hands, legs, blurred vision, headaches, confusion and also impaired speech patterns because of hypertension associated cerebral hemorrhage. The damage is caused predominantly in the ventricular region of the brain.
The symptoms associated with cerebral hemorrhage often lead to paralysis, seizures and sudden loss of consciousness, tingling sensation in the feet, altered taste patterns, nausea and inability to swallow. This happens because of ischemia or lack of blood supply to the brain which inevitably affects the neuromuscular activity of the body. In addition to these, cerebral hemorrhage also results due to liver damage or brain tumor.
Diagnosis
In case of head injury or trauma, the hematomas have to be removed as soon as possible with thorough evaluation of the damaged regions of the skull in association with the membranes to rule out all possibilities of internal organ bleeding or presence of any kind of blood clots. Patients are rushed in for radiological examinations to minimize the time required to intervene the situation of head injury as any delay can be fatal. In patients with hypertension and previous history of diabetes, thorough radiological examination is performed to identify the ischemic regions present in the brain. Abnormal blood vessels are corrected using interventional radiology.
Treatment options for cerebral hemorrhages are often associated with treatments pertaining to hypertension and diabetes. Patients are counseled to undergo corrective surgeries in case of hemorrhages associated with aneurysms.
At TargetWoman, every page you read is crafted by a team of highly qualified experts — not generated by artificial intelligence. We believe in thoughtful, human-written content backed by research, insight, and empathy. Our use of AI is limited to semantic understanding, helping us better connect ideas, organize knowledge, and enhance user experience — never to replace the human voice that defines our work. Our Natural Language Navigational engine knows that words form only the outer superficial layer. The real meaning of the words are deduced from the collection of words, their proximity to each other and the context.
Diseases, Symptoms, Tests and Treatment arranged in alphabetical order:

A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Bibliography / Reference
Collection of Pages - Last revised Date: February 23, 2026



